Creating and Using Macros
Getting Started
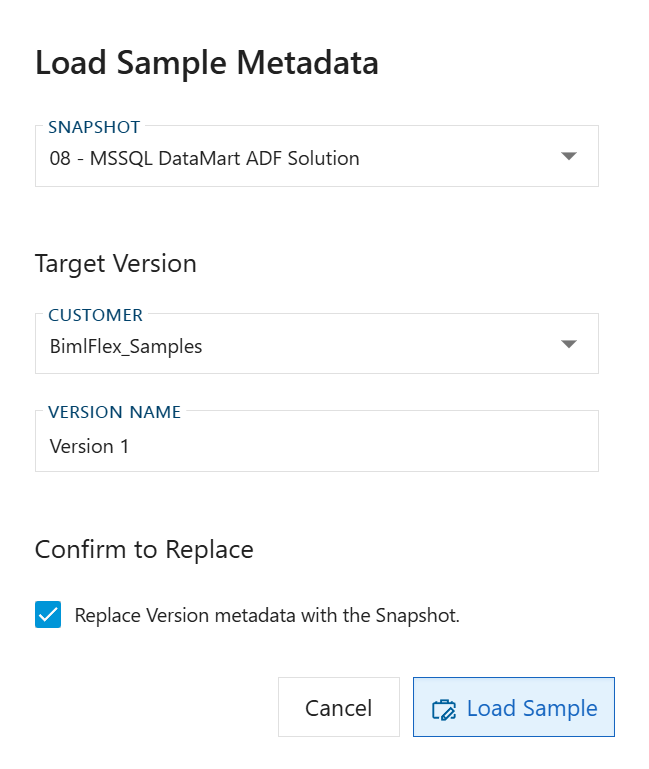
Step 1: Load Sample Metadata
-
Navigate to the BimlFlex sample collection
-
Select the "08 - MSSQL DataMart ADF Solution" sample
-
Load the sample metadata into your environment
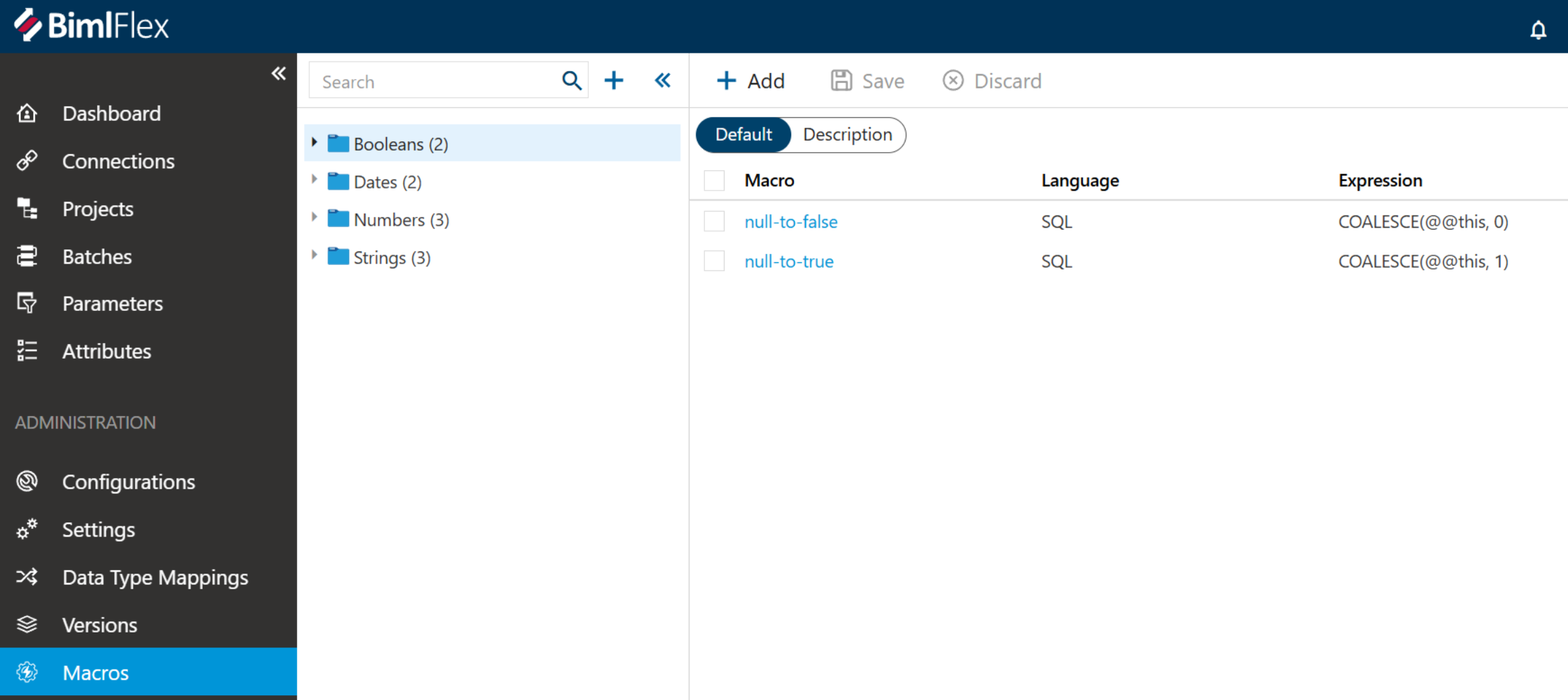
Step 2: Access the Macros Interface
-
Once the sample metadata is loaded, navigate to the Macros section
-
Review the existing macros included in the sample (these serve as examples for implementation)
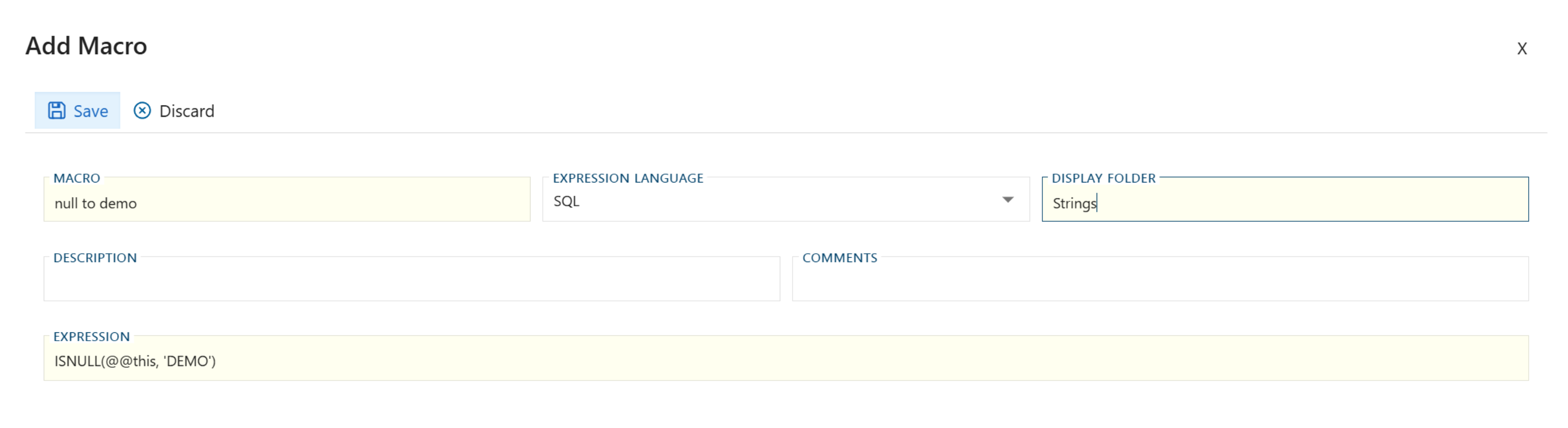
Creating a String Expression Macro
Step 3: Create a New Macro
- Click on the option to add a new string macro
- Enter a name for your macro (e.g., "null to demo")
- Add a description (optional)
- Add comments (optional)
- Enter the SQL expression:
ISNULL(@@this, 'DEMO')
- Save the macro
note
The @@this placeholder is context-aware and will automatically be replaced with the column name where the macro is applied. This eliminates the need to manually specify column names.
Applying Macros to Columns
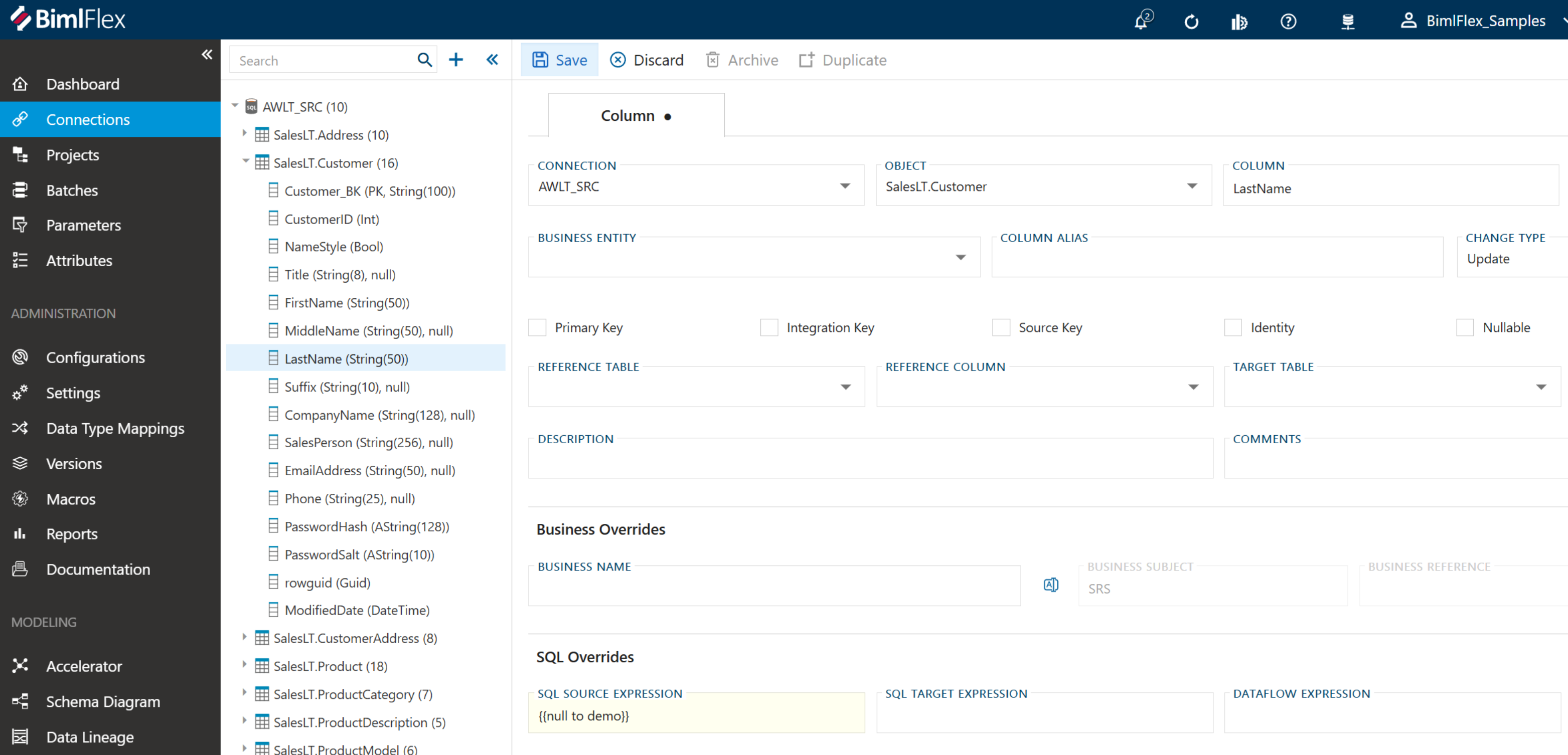
Step 4: Apply Column-Level Macro
- Navigate to your target table (e.g., Customer table view)
- Select the Columns section
- Choose the column where you want to apply the macro (e.g., "LastName")
- In the expression field, type {{ (two open curly brackets)
- Select your macro from the dropdown list
- Save the column configuration
Creating Join Statement Macros
Step 5: Create a Join Macro
- Create a new macro
- Name it descriptively (e.g., "product-category")
- Paste your join statement SQL code:
INNER JOIN [awlt].[ProductCategory] spc
ON sp.[ProductCategory_BK] = spc.[ProductCategory_BK]
INNER JOIN [awlt].[ProductModel] spm
ON sp.[ProductModel_BK] = spm.[ProductModel_BK]
- Save the macro
note
Macros can be nested within other macros, allowing you to build complex, reusable logic structures.
Step 6: Apply Join Macro to Table
- Return to your target table
- Navigate to the Join SQL field
- Type {{ (two open curly brackets)
- Select "product-category" from the dropdown
- Save the Object
Use Cases and Best Practices
Common Applications
- Default date logic: Create macros for frequently used date calculations
- Environment-specific WHERE clauses: Define standard filtering logic
- Standardized NULL handling: Implement consistent NULL replacement across tables
- Reusable join patterns: Store complex join logic for repeated use
Best Practices
- Use descriptive names for macros to ensure clarity
- Document macro purposes in the description field
- Test macros on a single column/table before widespread implementation
- Leverage nested macros for complex logic when appropriate
- Review generated code after build to verify correct injection
Conclusion
BimlFlex macros provide a powerful way to create reusable, maintainable SQL logic across your data integration projects. By implementing macros, you can:
- Reduce code duplication
- Ensure consistency across implementations
- Simplify maintenance and updates
- Improve development efficiency