Azure Data Factory Landing Area
When using an ELT ('pushdown') approach for data integration, BimlFlex creates a number of Execute Pipelines with various Stored Procedure calls and Copy Activities.
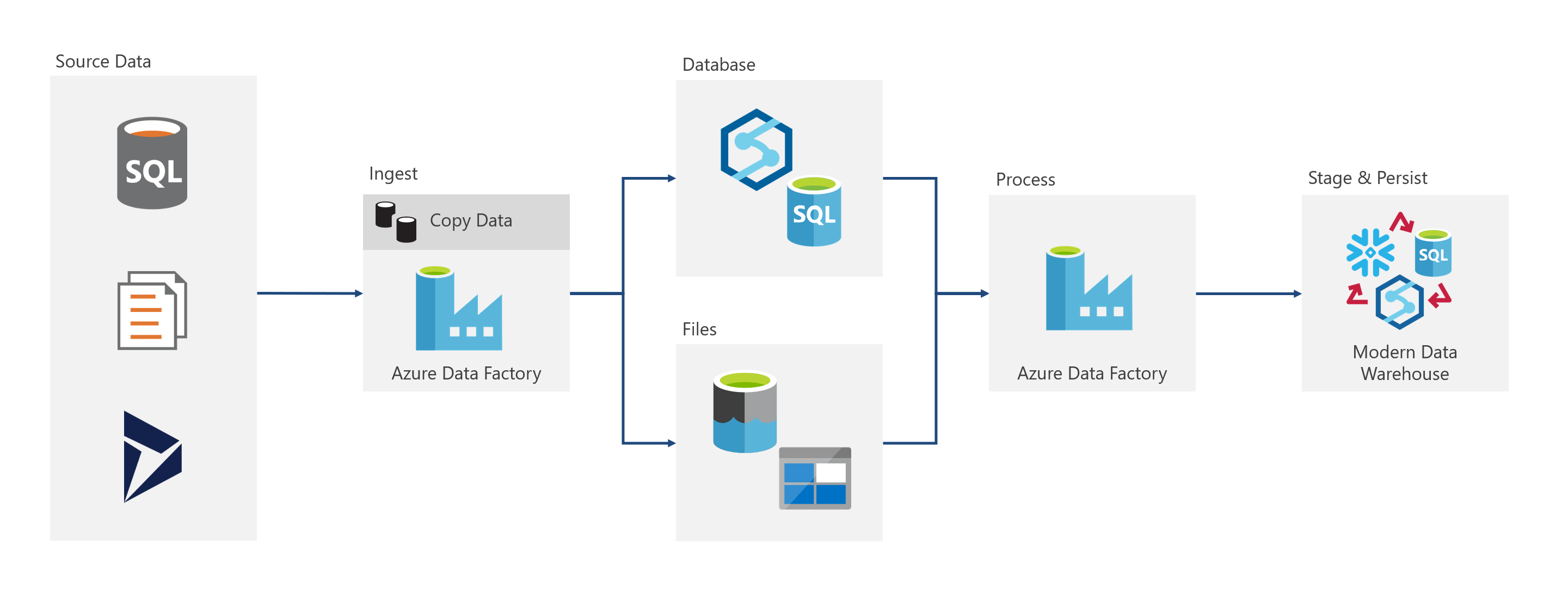
The Azure Data Factory (ADF) Copy Activity does not allow for transformations during the copying of the data. To support transformation of data using a Copy Activity, BimlFlex uses a Landing Area that is accessible by SQL-based Stored Procedures in the Staging Area.
This way, data can be accessed directly to perform any required transformations while the ADF Execute Pipeline can use the Copy Activity to efficiently move the results to the Staging Area.
The general architecture is below with the Landing Area in the middle, supporting either a database or files.
For additional details on ADF or the Copy activity refer to the below guides:
Microsoft Docs: Azure Data Factory documentation
Microsoft Docs: Copy Activity in Azure Data Factory
Configure a Landing Area By Example
This section walks through the common steps and considerations for creating and configuring the landing connection. This example uses sample metadata to configure an appropriate Landing Area for a Table-Based Configuration.
For addition details of alternate configurations refer to the detailed configuration section.
The Varigence YouTube channel contains various introduction videos about using BimlFlex and BimlStudio. This video walks through how to configure a Landing Area for Azure Data Factory using BimlFlex.
High Level Steps
- Start with a sample metadata set. This example uses the
01 - MSSQL Starting Point, which includes connections for a sample on-premises SSIS data solution including Batch and Project definitions - Archive the
BFX_DVandBFX_DMProject and Batches to minimize the amount of additional metadata that is visible in the app - Update the
EXT_AWLT_SRCextract Project to have the target set to the staging area connection,BFX_STG - Archive the
BFX_DVandBFX_DMConnections - Navigate to the Connections page, create a Landing connection by duplicating the BFX_STG connection
- Name the new connection
BFX_LND - Update the Integration Stagefor the Connection to
Landing Area
- Name the new connection
- Enable the connection for ADF use by switching on the CLOUD setting
- Enabling the connection for Cloud exposes the Linked Services configuration for the connection
- Update the source connection to use the
BFX_LNDconnection as the LANDING CONNECTION - Configure the Linked Service to use the appropriate configuration
- The video uses a pre-created Azure Key Vault to store the connection string information for the connections
- Add the Azure Key Vault as a configuration for the Linked Service
- Define the secret that the Linked Service should use as the connection string
- Reuse the Key Vault and secret configuration for each of the connections
- Reconfigure the
EXT_AWLT_SRCProject to generate ADF artifacts instead of SSIS projects by updating the Integration Template used
Importing Metadata
The example uses the 01 - MSSQL Starting Point metadata to generate Source System and Staging Area Connections.
For additional details on Importing Samples and Metadata refer to the below guides:
In order to proceed a Source System Connection and Staging Area Connection is needed.
The example could be followed along with using any supported Source System and any Stage Area that supports a Table-Based Configuration for the Landing Area (Microsoft SQL Server, Azure Synapse).
Cleaning (Illustration and Example Only)
The video archives multiple BimlFlex Entities to illustrate the minimal configuration needed to implement and configure a Landing Area. These are optional steps to streamline and minimize configuration.
Do not archive any BimlFlex Entities if following along with your own metadata.
Create a Landing Connection
When using a Table Based Configuration the Landing Area and Staging Area should share the same connection details. The easiest way to achieve this is by duplicating the Staging Area Connection, naming it appropriately and updating the Integration Stage to Landing Area.
In this configuration, the Landing Area is a conceptual separation via naming practice only. Ensure that the Catalog and Connection String for the Staging Area and Landing Area are the same.
Configure Linked Services
Azure Data Factory requires the use of Linked Services. These are defined as part of the Connection but are configured separately on each connection once enabled. For each connection that will be used by the ADF process, the Cloud field is required to be enabled in order to expose the configuration for the corresponding Linked Service.
The example uses a pre-created Azure Key Vault to manage the complete connection string through use of a Secret. With familiarly of Azure Key Vaults and the deployment environment, the Linked Services can be configured to suit individual sensitive information management practices.
For additional details on Linked Services, Azure Key Vaults and Sensitive Information Management refer to the below guides:
Configure the BimlFlex Project for ADF
The last step is to configure the BimlFlex Project to use the integration template of Azure Data Factory.
This step is performed last to ensure there are no validation errors when saving the Project.
The Azure Data Factory integration template requires all Connections to have cloud enabled.
The metadata is now configured to stage data via a Landing Area using Azure Data Factory.
Detailed Configuration
Depending to the system type of the Staging Area, the Landing Area can be configured as either a group of database tables or a blob storage. The below table for outlines the supported Landing Area configurations for each supported Staging Area.
Use the below selectors to configure documentation for the desired scenario.
Synapse Analytics
Configured for Azure Synapse Analytics.
Microsoft SQL Server
Configured for Microsoft SQL Server.
Snowflake
Configured for Snowflake.
Available Landing Area configurations.
Table Landing
Configured for a table based landing.
Table Landing
Configured for a table landing.
Blob PolyBase Landing
Configured for Azure Blob PolyBase landing.
Blob Landing
Configured for Azure Blob landing.
Details
It is important to note that although the Landing Area is configured as a separate BimlFlex Connection, in a Table Based Configuration it should be considered the same database as the Staging Area. As such the Landing Area does not deploy separately, and instead deploys with the Staging Area.
A Table Based Configuration requires the Landing Area to be in the same database as the Staging Area. Ensure the connection string, catalog and applicable Linked Service configurations are identical to that of the Staging Area Connection.
When using a Table-Based Configuration, the Landing Area is a group of tables separated through use of naming conventions. By default the Landing Area tables will have a land_ prefix appended to all landing tables.
The prefix appended to landing tables can be configured by updating the Append Name Landing BimlFlex Setting in the Staging Naming group.
The default configuration is land.
Details
A Blob Landing Configuration requires a Blob Container for Staging, Archive and Error. These Blob Containers can be hosted inside a single Azure Storage Account or a unique account for each. Once the Azure artifacts are created, the appropriate settings for each account will need to be populated.
Details
A PolyBase Landing Configuration requires a Blob Container for Staging, Archive and Error. These Blob Containers can be hosted inside a single Azure Storage Account or a unique account for each. Once the Azure artifacts are created, the appropriate settings for each account will need to be populated.
Additionally the Azure Copy Settings will need to be configured as such:
- Set the copy method to
PolyBase - Configure Polybase settings as needed
- Recommend you use the following value if unsure:
RejectType="Value" RejectValue="0" UseTypeDefault="false"
- Recommend you use the following value if unsure:
EnableEnable Staging- Configure the staging settings
- Recommend you use the following value if unsure:
LinkedServiceName="@@this" EnableCompression="false" Path="staging"
- Recommend you use the following value if unsure:
- (Optional)
EnableEnable Logging - (Optional) Configure log settings
- Recommend you use the following value if unsure:
LinkedServiceName="@@this" LogLevel="Warning" Path="log"
- Recommend you use the following value if unsure:
For additional details on configuring a PolyBase Connection see the below guides:
- Synapse Implementations - Connection Details
- See ADF configuration for
Landing Area (LND)andPolyBase Connection (PLY)
- See ADF configuration for
- Copy and transform data in Azure Synapse Analytics by using Azure Data Factory
Relevant Settings
The following Azure Settings are used to configure the table destinations.
- Staging Naming\Naming - configures naming patterns for Landing Tables and other Staging Objects
Relevant Settings
The following Azure Settings are used to configure the blob destinations.
- Azure Storage\Processing -configures the details for relevant containers
- Azure Storage\Settings- Configures the blob storage domain
Relevant Settings
The following Azure Settings are used to configure the PolyBase blob destinations.
- Azure Storage\Processing -configures the names Accounts, Container Names and Keys/Tokens to be used with the Blob destination for AzCopy
- Azure Storage\Settings -configures the blob storage domain
- Azure Copy\Copy Method - configures the copy method and Polybase settings
- Azure Copy\Advanced Settings - enables and configures PolyBase Staging and Logging
For additional details on Blob Storage refer to the below guides: